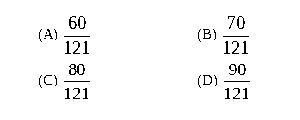Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering - GATE 2012
Last Date : 17 October 2011 (Apply Online)
Start Date : 12 September 2011
Organizing Institute : Indian Institute of Technology Delhi
Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering (GATE) is an all India examination administered and conducted jointly by the Indian Institute of Science and seven Indian Institutes of Technology on behalf of the National Coordination Board - GATE, Department of Higher Education, Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD), Government of India.
Candidates have to Apply only ONLINE. The application fee is Rs 1000/- for GENERAL/OBC/ category and Rs 500/- for SC/ST/PD category candidates.
Date of Online Examination: 29-01-2012 (Sunday)
Date of Offline Examination: 12-02-2012 (Sunday)
SYLLABUS/SCHEME OF EXAMINATION FOR GATE - 2012
A candidate can apply for only ONE of the 21 papers listed in the table given below. In the tables given below, the columns titled 'Paper Title' and 'Title of the Section' provide links to the appropriate syllabus.
The choice of the appropriate paper is the responsibility of the candidate. Some guidelines in this respect are suggested below.
The candidate is expected to appear in a paper appropriate to the discipline of his/her qualifying degree. The candidate is, however, free to choose any paper according to his/her admission plan, keeping in mind the eligibility criteria of the institutions in which he/she wishes to seek admission.
Requests for change of GATE Examination paper after the submission of Application Form will not be considered.
Code Paper Title
AE Aerospace Engineering
AG Agricultural Engineering
AR Architecture and Planning
BT Biotechnology
CE Civil Engineering
CH Chemical Engineering
CS Computer Science and Information Technology
CY Chemistry
EC Electronics and Communication Engineering
EE Electrical Engineering
GG Geology and Geophysics
IN Instrumentation Engineering
MA Mathematics
ME Mechanical Engineering
MN Mining Engineering
MT Metallurgical Engineering
PH Physics
PI Production and Industrial Engineering
TF Textile Engineering and Fibre Science
XE Engineering Sciences
XL Life Sciences
XE (Engineering Sciences) and XL (Life Sciences) papers are of general nature and will comprise of the sections listed below. A candidate appearing in XE or XL paper will be required to answer three sections apart from the General Aptitude (GA) questions. Section A is compulsory in XE paper and Section H is compulsory in XL paper. The candidate can choose any two out of the remaining sections listed against the respective papers, at the time of examination
===============================
XE: Engineering Sciences
---------------------------
Paper Section Title of the Section
XE A Engineering Mathematics (Compulsory)
XE B Fluid Mechanics
XE C Materials Science
XE D Solid Mechanics
XE E Thermodynamics
XE F Polymer Science and Engineering
XE G Food Technology
----------------------------------
---------------------------------
XL: Life Sciences
-----------------------------------
Paper Section Title of the Section
XL H Chemistry (Compulsory)
XL I Biochemistry
XL J Botany
XL K Microbiology
XL L Zoology
XL M Food Technology
-------------------------------
=======================================
The GATE examination consists of a single paper of 3 hours duration which contains 65 questions carrying a maximum of 100 marks. The question paper will consist of only objective questions. In all papers other than AE, AG, AR, GG, MN and TF, all the questions are of multiple choice type. In AE, AG, AR, GG, MN and TF papers, the question paper will consist of questions of multiple choice type and also some questions of numerical answer type. For multiple choice type questions, each question will have four choices for the answer. For numerical answer type questions, each question will have a number as the answer. See below to view the pattern of question papers. The examination for the papers with codes AE, AG, AR, GG, MN and TF will be carried out ONLINE using computers where the candidates will be required to enter the answer for each question using mouse. For all other papers, the candidates will have to mark the correct choice on an Optical Response Sheet (ORS) by darkening the appropriate bubble against each question. There will be negative marking for each wrong answer, except for the numerical answer type questions.
Each GATE paper shall have a General Aptitude (GA) component carrying 15 marks
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Pattern of Question Papers and Marking
The examination for the papers with codes AE, AG, AR, GG, MN and TF will be carried out ONLINE using computers where the candidates will be required to enter the answer for each question using mouse. For all other papers, the candidates will have to mark the correct choice on an Optical Response Sheet (ORS) by darkening the appropriate bubble against each question.
In the ONLINE papers, the question paper will consist of questions of multiple choice type and numerical answer type. For multiple choice type questions, each question will have four choices for the answer. For numerical answer type questions, each question will have a number as the answer and choices will not be given.
GATE 2012 would contain questions of four different types in various papers:
Multiple choice questions carrying 1 or 2 marks each.
Common data questions, where two successive questions use the same set of input data.
Linked answer questions, where the answer to the first question of the pair is required in order to answer its successor.
Numerical answer questions, where the answer is a number, to be entered by the candidate.
Examples of such questions can be found in Question Types.
In all the papers, there will be a total of 65 questions carrying 100 marks, out of which 10 questions carrying 15 marks in General Aptitude (GA) are compulsory.
In the papers bearing the codes AE, AG, BT, CE, CH, CS, EC, EE, GG, IN, ME, MN, MT, PI, TF and XE, the Engineering Mathematics will carry 15 % of the total marks, the General Aptitude section will carry 15 % of the total marks and the remaining 70 % of the total marks is devoted to the subject of the paper.
In the papers bearing the codes AR, CY, GG, MA, PH and XL, the General Aptitude section will carry 15 % of the total marks and the remaining 85 % of the total marks is devoted to the subject of the paper.
Marking
For 1 mark multiple choice questions, 1/3 mark will be deducted for a wrong answer. Likewise, for 2 marks multiple choice questions, 2/3 mark will be deducted for a wrong answer. However, for the linked answer question pair, where each question carries 2 marks, 2/3 mark will be deducted for a wrong answer to the first question only. There is no negative marking for wrong answer to the second question of the linked answer question pair. If the first question in the linked pair is wrongly answered or is unattempted, then the answer to the second question in the pair will not be evaluated. There is no negative marking for numerical answer type questions.
Pattern of Question Papers
General Aptitude (GA) Section:
In all papers, GA questions are of multiple choice type, and carry a total of 15 marks. The GA section includes 5 questions carrying 1 mark each (sub-total 5 marks) and 5 questions carrying 2-marks each (sub-total 10 marks)
Question papers other than GG, XE and XL:
These papers would contain 25 multiple choice questions carrying one mark each (sub-total 25 marks) and 30 multiple choice questions carrying two marks each (sub-total 60 marks). Out of these, two pairs of questions would be common data questions, and two pairs of questions would be linked-answer questions. In the ONLINE papers, the question paper will consist of questions of multiple choice type and numerical answer type. For multiple choice type questions, each question will have four choices for the answer. For numerical answer type questions, each question will have a number as the answer and choices will not be given.
GG (Geology and Geophysics) Paper:
Apart from the General Aptitude (GA) section, the question paper consists of two parts: Part A and Part B. Part A is common for all candidates. Part B contains two sections: Section 1 (Geology) and Section 2 (Geo-physics). Candidates will have to attempt questions in Part A and either Section 1 or Section 2 in Part B.
Part A consists of 25 multiple choice questions carrying 1-mark each (sub-total 25 marks). Each section in Part B (Section 1 and Section 2) consists of 30 multiple choice questions carrying 2-marks each (sub-total 60 marks). Out of these, two pairs of questions would be common data questions, and two pairs of questions would be linked-answer questions.
XE Paper (Engineering Sciences):
In XE paper, Engineering Mathematics section (Section A) is compulsory. This section contains 11 multiple choice questions carrying a total of 15 marks: 7 questions carrying 1-mark each (sub-total 7 marks), and 4 questions carrying 2-marks each (sub-total 8 marks).
Each of the other sections of the XE paper (Sections B through G) contains 22 questions carrying a total of 35 marks: 9 questions carrying 1-mark each (sub-total 9 marks) and 13 questions carrying 2-marks each (sub-total 26 marks). Out of the 2-mark questions, 2 pairs are common data questions and 1 pair is linked answer questions.
XL Paper (Life Sciences):
In XL paper, Chemistry section (Section H) is compulsory. This section contains 15 multiple choice questions carrying a total of 25 marks: 5 questions carrying 1 mark each (sub-total 5 marks) and 10 questions carrying 2-marks each (sub-total 20 marks). Out of the 2-mark questions, 1 pair is common data questions, and 1 pair is linked answer questions.
Each of the other sections of the XL paper (Sections I through M) contains 20 multiple choice questions carrying a total of 30 marks: 10 questions carrying 1-mark each (sub-total 10 marks) and 10 questions carrying 2-marks each (sub-total 20 marks).
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GATE 2012 Question Types
Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple choice questions in all papers and sections will contain four answers, of which only one is correct. The types of questions in a paper may be based on following logic:
(i) Recall:
These are based on facts, principles, formulae or laws of the discipline. The candidate is expected to be able to obtain the answer either from his/her memory of the subject or at most from a one-line computation.
Example
Q. During machining maximum heat is produced
(A) in flank face (B) in rake face
(C) in shear zone (D) due to friction between chip and tool.
(ii) Comprehension:
These questions will test the candidate's understanding of the basics of his/her field, by requiring him/her to draw simple conclusions from fundamental ideas.
Example
Q. A DC motor requires a starter in order
(A) to develop a starting torque
(B) to compensate for auxiliary field ampere turns
(C) to limit armature current at starting
(D) to provide regenerative braking
(iii) Application:
In these questions, the candidate is expected to apply his/her knowledge either through computation or by logical reasoning.
Example:
Q. The sequent depth ratio of a hydraulic jump in a rectangular channel is 16.48. The Froude number at the beginning of the jump is:(A) 10.0 (B) 5.0
(C) 12.0 (D) 8.0
(iv) Analysis and Synthesis:
These can be linked questions, where the answer to the first question of the pair is required in order to answer its successor. Or these can be common data questions, in which two questions share the same data but can be solved independently of one another.
Common data questions
Example
Common Data, for instance, Questions 48 and 49 in main paper:
Let X and Y be jointly distributed random variables such that the conditional distribution of Y, given X=x, is uniform on the interval (x-1,x+1). Suppose E(X)=1 and Var(X)= 5/3
First question using common data:
Q.48 The mean of the random variable Y is
(A) 1/2 (B) 1 (C) 3/2 (D) 2
Second question using common data:
First question of the pair:
Q.52 The value of K which will cause sustained oscillations in the closed loop system is
Second question of the pair:
Q.53 The frequency of sustained oscillations is
The questions based on the above four logics may be a mix of single stand alone statement / phrase / data type questions, combination of option codes type questions or match items types questions.
========================================================
The examination for the papers with codes AE, AG, AR, GG, MN and TF will be carried out ONLINE using computers where the candidates will be required to enter the answer for each question using mouse. For all other papers, the candidates will have to mark the correct choice on an Optical Response Sheet (ORS) by darkening the appropriate bubble against each question.
In the ONLINE papers, the question paper will consist of questions of multiple choice type and numerical answer type. For multiple choice type questions, each question will have four choices for the answer. For numerical answer type questions, each question will have a number as the answer and choices will not be given.
GATE 2012 would contain questions of four different types in various papers:
- Multiple choice questions carrying 1 or 2 marks each.
- Common data questions, where two successive questions use the same set of input data.
- Linked answer questions, where the answer to the first question of the pair is required in order to answer its successor.
- Numerical answer questions, where the answer is a number, to be entered by the candidate.
Examples of such questions can be found in Question Types.
In all the papers, there will be a total of 65 questions carrying 100 marks, out of which 10 questions carrying 15 marks in General Aptitude (GA) are compulsory.
In the papers bearing the codes AE, AG, BT, CE, CH, CS, EC, EE, GG, IN, ME, MN, MT, PI, TF and XE, the Engineering Mathematics will carry 15 % of the total marks, the General Aptitude section will carry 15 % of the total marks and the remaining 70 % of the total marks is devoted to the subject of the paper.
In the papers bearing the codes AR, CY, GG, MA, PH and XL, the General Aptitude section will carry 15 % of the total marks and the remaining 85 % of the total marks is devoted to the subject of the paper
--------------------------------Marking
For 1 mark multiple choice questions, 1/3 mark will be deducted for a wrong answer. Likewise, for 2 marks multiple choice questions, 2/3 mark will be deducted for a wrong answer. However, for the linked answer question pair, where each question carries 2 marks, 2/3 mark will be deducted for a wrong answer to the first question only. There is no negative marking for wrong answer to the second question of the linked answer question pair. If the first question in the linked pair is wrongly answered or is unattempted, then the answer to the second question in the pair will not be evaluated. There is no negative marking for numerical answer type questions.
----------------------------------Pattern of Question Papers
General Aptitude (GA) Section: In all papers, GA questions are of multiple choice type, and carry a total of 15 marks. The GA section includes 5 questions carrying 1 mark each (sub-total 5 marks) and 5 questions carrying 2-marks each (sub-total 10 marks)
Question papers other than GG, XE and XL: These papers would contain 25 multiple choice questions carrying one mark each (sub-total 25 marks) and 30 multiple choice questions carrying two marks each (sub-total 60 marks). Out of these, two pairs of questions would be common data questions, and two pairs of questions would be linked-answer questions. In the ONLINE papers, the question paper will consist of questions of multiple choice type and numerical answer type. For multiple choice type questions, each question will have four choices for the answer. For numerical answer type questions, each question will have a number as the answer and choices will not be given.
GG (Geology and Geophysics) Paper: Apart from the General Aptitude (GA) section, the question paper consists of two parts: Part A and Part B. Part A is common for all candidates. Part B contains two sections: Section 1 (Geology) and Section 2 (Geo-physics). Candidates will have to attempt questions in Part A and either Section 1 or Section 2 in Part B.
Part A consists of 25 multiple choice questions carrying 1-mark each (sub-total 25 marks). Each section in Part B (Section 1 and Section 2) consists of 30 multiple choice questions carrying 2-marks each (sub-total 60 marks). Out of these, two pairs of questions would be common data questions, and two pairs of questions would be linked-answer questions.
XE Paper (Engineering Sciences): In XE paper, Engineering Mathematics section (Section A) is compulsory. This section contains 11 multiple choice questions carrying a total of 15 marks: 7 questions carrying 1-mark each (sub-total 7 marks), and 4 questions carrying 2-marks each (sub-total 8 marks).
Each of the other sections of the XE paper (Sections B through G) contains 22 questions carrying a total of 35 marks: 9 questions carrying 1-mark each (sub-total 9 marks) and 13 questions carrying 2-marks each (sub-total 26 marks). Out of the 2-mark questions, 2 pairs are common data questions and 1 pair is linked answer questions.
XL Paper (Life Sciences): In XL paper, Chemistry section (Section H) is compulsory. This section contains 15 multiple choice questions carrying a total of 25 marks: 5 questions carrying 1 mark each (sub-total 5 marks) and 10 questions carrying 2-marks each (sub-total 20 marks). Out of the 2-mark questions, 1 pair is common data questions, and 1 pair is linked answer questions.
Each of the other sections of the XL paper (Sections I through M) contains 20 multiple choice questions carrying a total of 30 marks: 10 questions carrying 1-mark each (sub-total 10 marks) and 10 questions carrying 2-marks each (sub-total 20 marks).
=================================================================The examination for the papers with codes AE, AG, AR, GG, MN and TF will be carried out ONLINE using computers where the candidates will be required to enter the answer for each question using mouse. For all other papers, the candidates will have to mark the correct choice on an Optical Response Sheet (ORS) by darkening the appropriate bubble against each question.
In the ONLINE papers, the question paper will consist of questions of multiple choice type and numerical answer type. For multiple choice type questions, each question will have four choices for the answer. For numerical answer type questions, each question will have a number as the answer and choices will not be given.
GATE 2012 would contain questions of four different types in various papers:
- Multiple choice questions carrying 1 or 2 marks each.
- Common data questions, where two successive questions use the same set of input data.
- Linked answer questions, where the answer to the first question of the pair is required in order to answer its successor.
- Numerical answer questions, where the answer is a number, to be entered by the candidate.
Examples of such questions can be found in Question Types.
In all the papers, there will be a total of 65 questions carrying 100 marks, out of which 10 questions carrying 15 marks in General Aptitude (GA) are compulsory.
In the papers bearing the codes AE, AG, BT, CE, CH, CS, EC, EE, GG, IN, ME, MN, MT, PI, TF and XE, the Engineering Mathematics will carry 15 % of the total marks, the General Aptitude section will carry 15 % of the total marks and the remaining 70 % of the total marks is devoted to the subject of the paper.
In the papers bearing the codes AR, CY, GG, MA, PH and XL, the General Aptitude section will carry 15 % of the total marks and the remaining 85 % of the total marks is devoted to the subject of the paper
------------Marking
For 1 mark multiple choice questions, 1/3 mark will be deducted for a wrong answer. Likewise, for 2 marks multiple choice questions, 2/3 mark will be deducted for a wrong answer. However, for the linked answer question pair, where each question carries 2 marks, 2/3 mark will be deducted for a wrong answer to the first question only. There is no negative marking for wrong answer to the second question of the linked answer question pair. If the first question in the linked pair is wrongly answered or is unattempted, then the answer to the second question in the pair will not be evaluated. There is no negative marking for numerical answer type questions.
-----------------Pattern of Question Papers
General Aptitude (GA) Section: In all papers, GA questions are of multiple choice type, and carry a total of 15 marks. The GA section includes 5 questions carrying 1 mark each (sub-total 5 marks) and 5 questions carrying 2-marks each (sub-total 10 marks)
Question papers other than GG, XE and XL: These papers would contain 25 multiple choice questions carrying one mark each (sub-total 25 marks) and 30 multiple choice questions carrying two marks each (sub-total 60 marks). Out of these, two pairs of questions would be common data questions, and two pairs of questions would be linked-answer questions. In the ONLINE papers, the question paper will consist of questions of multiple choice type and numerical answer type. For multiple choice type questions, each question will have four choices for the answer. For numerical answer type questions, each question will have a number as the answer and choices will not be given.
GG (Geology and Geophysics) Paper: Apart from the General Aptitude (GA) section, the question paper consists of two parts: Part A and Part B. Part A is common for all candidates. Part B contains two sections: Section 1 (Geology) and Section 2 (Geo-physics). Candidates will have to attempt questions in Part A and either Section 1 or Section 2 in Part B.
Part A consists of 25 multiple choice questions carrying 1-mark each (sub-total 25 marks). Each section in Part B (Section 1 and Section 2) consists of 30 multiple choice questions carrying 2-marks each (sub-total 60 marks). Out of these, two pairs of questions would be common data questions, and two pairs of questions would be linked-answer questions.
XE Paper (Engineering Sciences): In XE paper, Engineering Mathematics section (Section A) is compulsory. This section contains 11 multiple choice questions carrying a total of 15 marks: 7 questions carrying 1-mark each (sub-total 7 marks), and 4 questions carrying 2-marks each (sub-total 8 marks).
Each of the other sections of the XE paper (Sections B through G) contains 22 questions carrying a total of 35 marks: 9 questions carrying 1-mark each (sub-total 9 marks) and 13 questions carrying 2-marks each (sub-total 26 marks). Out of the 2-mark questions, 2 pairs are common data questions and 1 pair is linked answer questions.
XL Paper (Life Sciences): In XL paper, Chemistry section (Section H) is compulsory. This section contains 15 multiple choice questions carrying a total of 25 marks: 5 questions carrying 1 mark each (sub-total 5 marks) and 10 questions carrying 2-marks each (sub-total 20 marks). Out of the 2-mark questions, 1 pair is common data questions, and 1 pair is linked answer questions.
Each of the other sections of the XL paper (Sections I through M) contains 20 multiple choice questions carrying a total of 30 marks: 10 questions carrying 1-mark each (sub-total 10 marks) and 10 questions carrying 2-marks each (sub-total 20 marks).
========================================Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple choice questions in all papers and sections will contain four answers, of which only one is correct. The types of questions in a paper may be based on following logic:
(i) Recall:
These are based on facts, principles, formulae or laws of the discipline. The candidate is expected to be able to obtain the answer either from his/her memory of the subject or at most from a one-line computation.
Example
Q. During machining maximum heat is produced
(A) in flank face (B) in rake face
(C) in shear zone (D) due to friction between chip and tool.
(ii) Comprehension:
These questions will test the candidate's understanding of the basics of his/her field, by requiring him/her to draw simple conclusions from fundamental ideas.
Example
Q. A DC motor requires a starter in order
(A) to develop a starting torque
(B) to compensate for auxiliary field ampere turns
(C) to limit armature current at starting
(D) to provide regenerative braking
(iii) Application:
In these questions, the candidate is expected to apply his/her knowledge either through computation or by logical reasoning.
Example:
Q. The sequent depth ratio of a hydraulic jump in a rectangular channel is 16.48. The Froude number at the beginning of the jump is:(A) 10.0 (B) 5.0
(C) 12.0 (D) 8.0
(iv) Analysis and Synthesis:
These can be linked questions, where the answer to the first question of the pair is required in order to answer its successor. Or these can be common data questions, in which two questions share the same data but can be solved independently of one another.
-------------------------------
Common data questions
Multiple questions may be linked to a common data problem, passage and the like. Two or three questions can be formed from the given common data problem. Each question is independent and its solution obtainable from the above problem data/passage directly. (Answer of the previous question is not required to solve the next question). Each question under this group will carry two marks.
Example
Common Data, for instance, Questions 48 and 49 in main paper:
Let X and Y be jointly distributed random variables such that the conditional distribution of Y, given X=x, is uniform on the interval (x-1,x+1). Suppose E(X)=1 and Var(X)= 5/3
First question using common data:
Q.48 The mean of the random variable Y is
(A) 1/2 (B) 1 (C) 3/2 (D) 2
Second question using common data:------------------------------------------------------------------
Syllabus for Aerospace Engineering (AE)
Engineering Mathematics
Linear Algebra:
Matrix algebra, systems of linear equations, eigen values and eigen vectors.
Calculus:
Functions of single variable, limit, continuity and differentiability, mean value theorems, evaluation of definite and improper integrals, partial derivatives, total derivative, maxima and minima, gradient, divergence and curl, vector identities, directional derivatives, line, surface and volume integrals. Theorems of Stokes, Gauss and Green.
Differential Calculus:
First order linear and nonlinear equations, higher order linear ODEs with constant coefficients, Cauchy and Euler equations, initial and boundary value problems, Laplace transforms. Partial differential equations and separation of variables methods.
Numerical methods:
Numerical solution of linear and nonlinear algebraic equations, integration by trapezoidal and Simpson rule, single and multi-step methods for differential equations.
Flight Mechanics
Atmosphere:
Properties, standard atmosphere. Classification of aircraft. Airplane (fixed wing aircraft) configuration and various parts.
Airplane performance:
Pressure altitude; equivalent, calibrated, indicated air speeds; Primary flight instruments: Altimeter, ASI, VSI, Turn-bank indicator. Drag polar; take off and landing; steady climb & descent,-absolute and service ceiling; cruise, cruise climb, endurance or loiter; load factor, turning flight, V-n diagram; Winds: head, tail & cross winds.
Static stability:
Angle of attack, sideslip; roll, pitch & yaw controls; longitudinal stick fixed & free stability, horizontal tail position and size; directional stability, vertical tail position and size; dihedral stability. Wing dihedral, sweep & position; hinge moments, stick forces.
Dynamic stability:
Euler angles; Equations of motion; aerodynamic forces and moments, stability & control derivatives; decoupling of longitudinal and lat-directional dynamics; longitudinal modes; lateral-directional modes.
Space Dynamics
Central force motion, determination of trajectory and orbital period in simple cases. Orbit transfer, in-plane and out-of-plane. Elements of rocket motor performance.
Aerodynamics
Basic Fluid Mechanics:
Incompressible irrotational flow, Helmholtz and Kelvin theorem, singularities and superposition, viscous flows, boundary layer on a flat plate.
Airfoils and wings:
Classification of airfoils, aerodynamic characteristics, high lift devices, Kutta Joukowski theorem; lift generation; thin airfoil theory; wing theory; induced drag; qualitative treatment of low aspect ratio wings.
Viscous Flows:
Flow separation, introduction to turbulence, transition, structure of a turbulent boundary layer.
Compressible Flows:
Dynamics and Thermodynamics of I-D flow, isentropic flow, normal shock, oblique shock, Prandtl-Meyer flow, flow in nozzles and diffusers, inviscid flow in a c-d nozzle, flow in diffusers. subsonic and supersonic airfoils, compressibility effects on lift and drag, critical and drag divergence Mach number, wave drag.
Wind Tunnel Testing:
Measurement and visualisation techniques.
Structures
Stress and Strain:
Equations of equilibrium, constitutive law, strain-displacement relationship, compatibility equations, plane stress and strain, Airy's stress function.
Flight Vehicle Structures:
Characteristics of aircraft structures and materials, torsion, bending and flexural shear. Flexural shear flow in thin-walled sections. Buckling. Failure theories. Loads on aircraft.
Structural Dynamics:
Free and forced vibration of discrete systems. Damping and resonance. Dynamics of continuous systems.
Propulsion
Thermodynamics of Aircraft Gas Turbine engines, thrust and thrust augmentation.
Turbomachinery:
Axial compressors and turbines, centrifugal pumps and compressors.
Aerothermodynamics of non rotating propulsion components:
Intakes, combustor and nozzle. Thermodynamics of ramjets and scramjets. Elements of rocket propulsion
Q.49 The variance of the random variable Y is
(A) 1/2 (B) 2/3 (C) 1 (D) 2
Q.49 The variance of the random variable Y is
(A) 1/2 (B) 2/3 (C) 1 (D) 2
Linked answer questions:
These questions are of problem solving type. A problem statement is followed by two questions based on the problem statement. The two questions are designed such that the solution to the second question depends upon the answer to the first one. In other words, the first answer is an intermediate step in working out the second answer. Each question in such linked answer questions will carry two marks. Example:
Statement for Linked Answer Questions, for instance, for Questions 52 and 53 in Main Paper:
The open loop transfer function of a unity feedback control system is given by